The building is an ancient human activity. It commenced with the full sensible need of a managed surroundings to mitigate the results of climate. Built-in shelters have been a capacity by using which man could adapt to various environments and grow to be world-class. There are different parts of the building, like foundation, plinth, stairs, floors, and roofs, etc. These elements of building structure provide connectivity, movement, and protection to the whole building structure.
What is Building?
As per definition.net a structure with a roof and walls stands more or less permanently in one place. The building’s fundamental feature is to provide a sensible structure and managed the environment to accommodate and protect residents and objects. If this primary function cannot be achieved, it is because some elements of the building have failed.
Parts of Building
The basic parts of the building structure are described below.
- Foundation
- Plinth
- Damp-proof Course
- Floor
- Walls
- Columns
- Beams
- Roof
- Stairs
- Lintels
- Doors and windows
- Parapet
- Building Services
Foundation
The foundation of a structure is built continuously under the surface to increase the structure’s background stability. It contains and builds up part of the underground structure level so that the backside strip can provide a sturdy and level floor to transfer the structure’s load over a large area of soil. The stable ground on which the foundation rests is known as the foundation bed.
Read Also: Different Types of Foundations and Their Uses
Plinth
The building’s plinth is part of the superstructure between the ground level (soil top surface that was prepared and leveled before the structure) and the building’s floor level (the lower floor).
A plinth height is provided primarily to protect the superstructure from dampness that can sink due to direct contact with the ground. It also prevents stormwater from entering the building directly in the event of heavy rain. Plinth levels are usually provided at approximately 300–450 mm above the finished surface. The plinth level should be decided by considering the upper part of the road surface, and the plinth should be kept at least 150 mm high.
Damp-proof Course
The damp proof course is a barrier usually formed by a membrane built into the walls of a building, typically about 15 centimeters above ground level.
Floor
The surface on which we carry out most activities—lay flooring on the filler of the base and the subsequent floor. The floor can be made of different materials, but the ground under the floor must be compacted. The floor is laid to prevent moisture from rising to the top, and there is a stable platform that can maintain hygiene and cleanliness.
Wall
Walls are basic parts of the building, that is a continuous vertical surface used to separate enclosed spaces. The walls can be constructed of bricks or concrete. The wall bears the load of the beam, floor, or roof above.
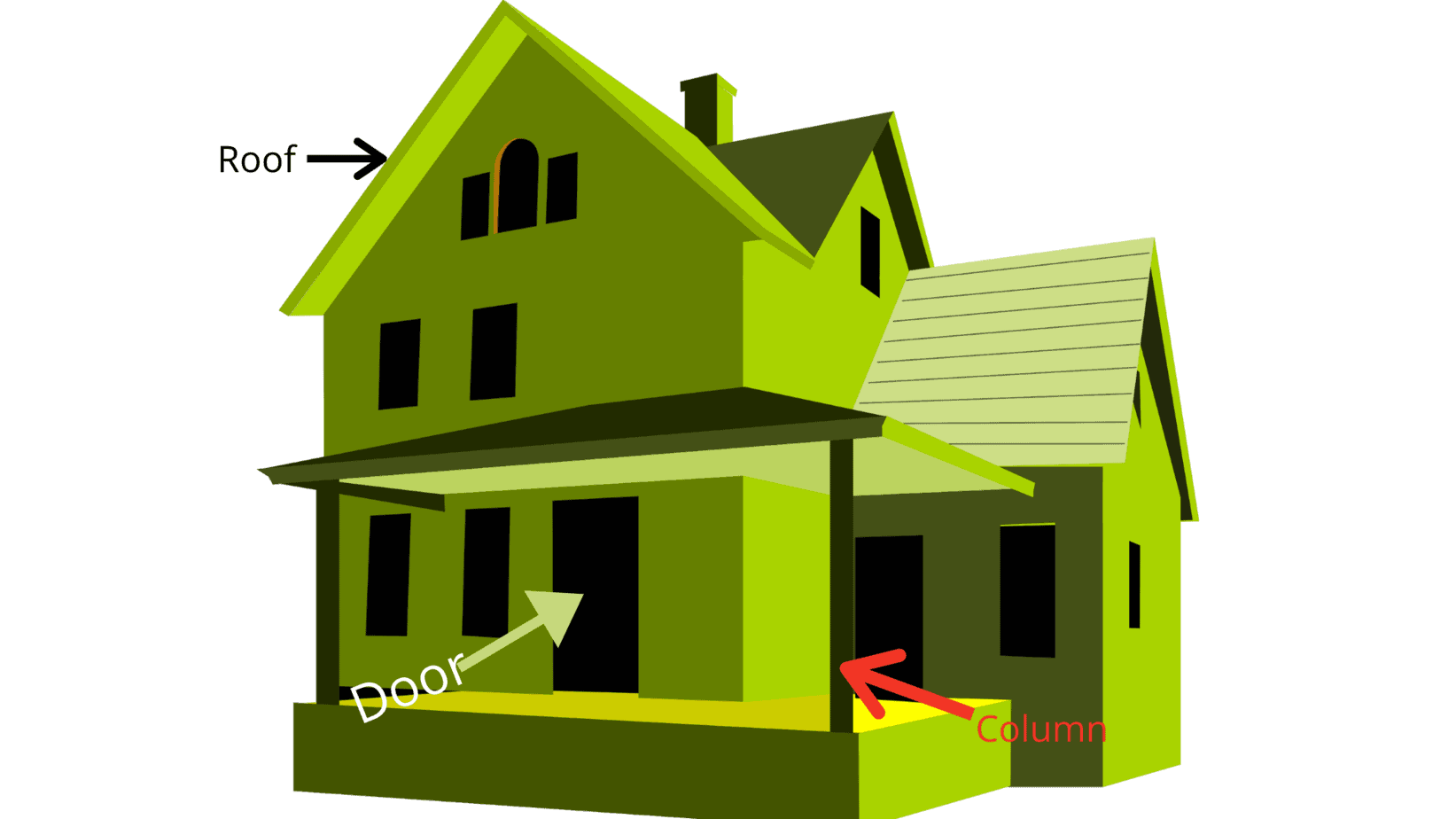
Column
The column is a vertical structural member, which mainly bears the compressive load. Since a building’s safety depends on the column’s strength, it is considered the most critical structural component in the building.
The column’s failure will cause the building to collapse gradually, and this will not happen when other components fail. The columns transfer vertical loads from the ceiling, floor, or roof slabs or beams to the floor or foundation. They also carry a bending moment around one or two cross-sectional axes.
Beam
The beam is a horizontal structural member that spans the distance between one or more supports. Beam contains a vertical load on its longitudinal axis (perpendicular to) the longitudinal bearing, which can bear the load primarily by resisting bending.
A beam is a laterally stressed member, and its cross-sectional dimension is small compared to its length. The beam is a structural component that carries the load of the slab. The beam transfers the load of the slab to the column.
Roof
The roofs are vital parts of the building. The most crucial element in the building is “a roof above the head.” The roof is a layer that covers the structure from the top. It can additionally stop structures and residents from being adversely affected by the environment.
Depending on the available funds and climatic conditions, we can use different kinds of roofs. The roof can be sloped or flat. Today, many types of roofs and roofing materials can be used.
The roof structure’s design has to withstand the static load imposed by the roof and frame, as nicely as the wind’s force. In some areas, it can also stand up to snow or flying dust. The roof has to be leak-proof and durable. It may also have to meet other requirements, such as fire resistance, proper thermal insulation, or high heat capacity.
Stairs
Stairs are a necessary part of the building, leading to different floors and roofs of the building. It consists of steps and steps between one or more intermediate layers.
Lintels
Lintels are beams that built an upside of openings in structures such as doorways and windows to support the higher structure load. The door beam’s width is equal to the wall’s width, and its ends are embedded in the wall. Lintels are categorized under their construction materials.
Doors and windows
The door provides a connecting link between rooms, allowing free movement between rooms. The wall opened the window. Doors and windows can provide lighting, smooth sound, and ventilation of the external environment.
Undoubtedly, both provide security and privacy. Different buildings have doors of various sizes; for example, doors in residential areas are entirely different from industrial buildings.
Parapet
A parapet is a low or low wall constructed along the edges of roofs, terraces, sidewalks, balconies, etc. The retaining wall can be built with special materials, such as strengthened cement concrete, steel, aluminum, glass, etc.
Parts of building Services
Building services are systems set up in building structures to make them comfortable, functional, environmentally friendly, and safe. The essential feature of buildings is to provide shelter for residents.
However, in our present-day world, all buildings’ design should provide an environment for humans to feel comfortable, work, stay, and achieve. Basically, “building services” are the elements that make buildings come to life, even the factors of the building’s operation. They contribute extensively to the sustainability of the building.