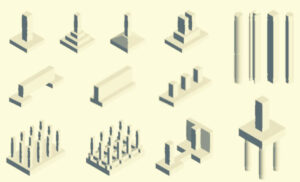
Types of pile foundation are categorized in the based different manners like as per material, as per function, as per the construction method.
Pile foundation falls under the type of deep foundations. It uses in that projects where a structure has a heavy load and soil cannot bear the load near the surface.
Classification of Pile Foundation
There are many methods to classify the pile foundations. They are classified based on the function they serve, materials, and installation process. The types of pile foundations are as follows.
Types of Pile Foundation Based on Function
- Sheet Piles
- Load bearing piles
- End bearing piles
- Friction piles
- Soil compactor piles
- Anchor Piles
- Batter Piles
Types of Pile Foundation Based on the Materials
- Concrete piles
- Timber piles
- Steel piles
- Composite piles
Types of Pile Foundation Based on the Construction Method
- Driven Piles
- Screw Piles
- Jacked Piles
- Bored Piles
Types of Pile Foundations Based on Function
Sheet Piles
If a pile is to provide the lateral support to the structure, then sheet piles are used. The load acting on the structure is in the form of flowing water and the pressure from loose soil. They cannot provide the load-bearing capacity in the vertical direction.
The main purposes of constructing them are the construction of retaining walls, to protect a structure from bak erosion, to acts against the loose soil around the trenches of the foundation, to isolate the foundation from the nearby soils, for stiffening the soil or to increase the bearing capacity of the soil.
Load Bearing Piles
This type of pile foundation’s main aim is mainly to transfer the vertical loads of the structure to the foundation below. The load is taken by the layer, which is strong enough to bear the structure’s load. Moreover, depending on the load transfer mechanism, the load-bearing piles can further be divided into end bearing piles and friction piles.
End bearing piles
The load taken by this type of pile passes through the tip of the pile. The lower portion of the pile usually rests on the bedrock, which is a strong layer to take the load from the top of the structure to it.
Sometimes, there may be a transition layer between the strong bedrock and the weak layer. So a pile acts as a column that can take the load and transfer to the bottom. Its total capacity can be calculated by multiplicating the bearing capacity of the soil and area of the pile. The diameter of the pile is calculated afterwards by considering a high factor of safety.
Friction pile
This type of pile foundation is based on the load transfer through the piles’ surface and soil surrounding the pile area. The surrounding materials around the piles are in the form of stiff clay and sandy soil. The frictional forces may be present throughout the pile’s length or may be present at some intervals around the pile depth, which depends on the soil’s strata.
In the case of friction piles, the entire piles act to transfer loads to the soil. The pile’s capacity is calculated by the multiplication of surface area and the frictional force developed per unit area. The capacity, diameter, and the number of piles can be increased if piles’ capacity increases.
Soil Compactor Piles
In the case, where the pile bearing capacity is to be increased, piles are constructed at the close spaces, by properly compacting the soil.
Types of Pile Foundation Based on the Materials
Timber piles
These types of pile foundation are placed below the water level. The service life of such piles is about 30 years. The shape can be rectangular or circular. The diameter varies from 12’’ to 16’’. The length of such piles is 20 times the width at the top of the pile. The designed load for such a pile is 15 to 20 tons. The strength of piles can be increased by the bolting the sides of piles by fish plates.
Advantages of timber piles
- They are available in regular sizes available.
- They are economical.
- Easy to place the piles in place.
- The damage possibility of the piles is very less.
- The length can be cut off at any depth wherever they are required.
- They can be easily removed from the site in case of replacement or removal.
Disadvantages of timber piles
- They are not available in long lengths.
- The straight piles are difficult to obtain if the length is too long.
- If the soil beneath the pile foundation is very hard, then penetrating the pile to the soil is not an easy process.
- The timber piles cannot be used as end-bearing piles.
- To increase the piles’ durability, they are treated with the preservatives to increase the resistance towards external factors.
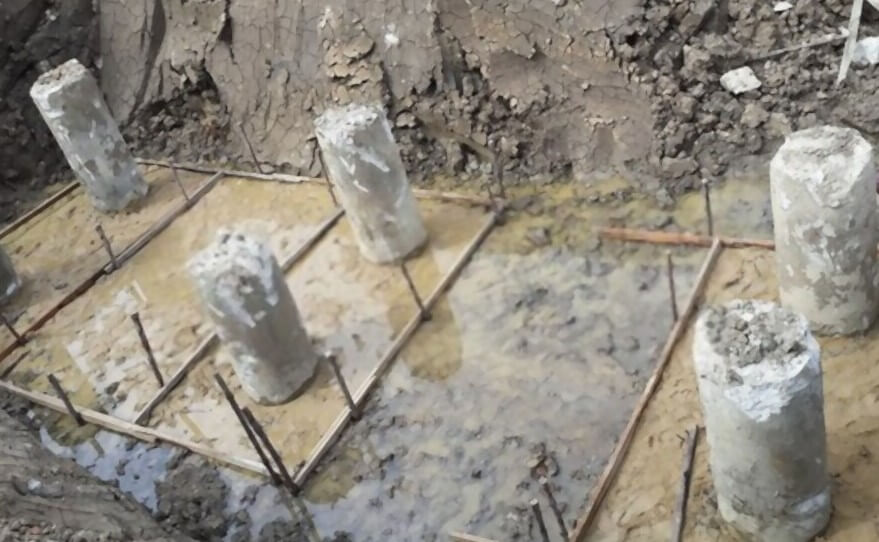
Concrete Piles
Precast Concrete Piles
The piles are cast in the horizontal form if they are rectangular in shape. They are driven vertically into the ground. They are usually reinforced with steel reinforcement to overcome the breakage during transportation from the bed location to site, where it is to be installed. After the pile construction, proper curing is done in complete 28 days, so that the pile can gain strength effectively.
Advantages
- The resistance towards chemical and biological cracks is very high.
- The strength of such a pile is very high.
- The driving of the pile may be done by placing pipe at the centre of the pile.
- The pace of work can be increased if the pile are constructed before the pile driving phase.
- The confinement of the pile is usually ensured.
- The quality can be controlled.
- They can also be driven underwater at larger depths.
- The load-bearing of the piles is started once they are installed into the ground.
Disadvantages
- Once the construction phase of piles has started, it is very difficult to accommodate changes in the piles’ length.
- The movement of piles is very difficult.
- The equipment used to move and drive them into the ground should be heavy.
- A delay in the project might occur if they are not available readymade.
- The piles can break or damaged the process of driving and handling them at the site.
Read Also: Cast in situ or Precast Concrete! Which one is a Better method
Cast in place Concrete Piles
This pile is made by boring soil up to the required level of depth, and then the fresh concrete is poured in the ground. The procedure consists of driving a sheet or steel shell into the ground and then pouring concrete in it and then the shell is pulled out during the pouring of concrete.
Advantages
- The metallic sheets are usually light in weight and easily handled at the site.
- Their length is varied.
- The metallic shells can be made together at the site.
- No extra reinforcement is required to overcome the handling damage.
- There is almost no possibility of breaking during the installation process.
- The number of piles can easily be increased if required.
Disadvantages
- Their installation requires specific care and control at the site.
- Sufficient space is required for material storage.
- When the underground flow of water is very high, then concreting the cast in situ piles is very difficult.
- The pile shape would be such that the bottom of the pile may not be symmetrical.
- If the reinforcement is not used and the casing is not used while concreting the piles, then the piles’ failure may occur due to uplifting force, and it may fail in tension.
Steel Piles
The piles’ section maybe I shape, or it may be in the form of a hollow pipe. They are usually poured in concrete. The diameter range of steel piles is usually 10’’ to 24’’ and thickness in ¾ inches. The driving process of piles is straightforward as the cross-sectional area of the pile is minimal. The most used application of steel pile is as end-bearing piles.
Advantages of steel piles
- The installation process of these types of pile foundation is easy.
- The depth of such a pile can be increased as compared to the top of other piles.
- They can pass through the soil interface easily, whether it is hard soil or soft soil.
- Their load-bearing capacity is very high.
Composite piles
Composite pile refers to the mutual driving of two piles of different materials so that they work together to perform the function of a single pile.
Types of Piles Based on the Construction Method
Driven Piles
Driven piles are precast piles using concrete. Wood or steel. Use a vibratory hammer (pile driver) to drive this type of pile into the soil.
Driven piles are also called displacement piles. They are used as the foundation for the structure to provide support.
Driven piles provide lateral support for the retaining wall. An impact hammer or vibratory hammer is used to advance the pile to the design tip depth or nominal resistance and is usually installed in groups and tied in the pile cap.
Screw Piles
The screw pile is wound on the ground, just like a screw is wound on wood. This is an effective installation method, combined with its load distribution mechanism, to provide effective ground performance in a variety of soils (including seismic zones with liquefaction potential).
A powerful hydraulic motor is used to apply the high torque required to screw the screw pile into the ground. The motor is fixed on the loading and unloading machine, and the size range of the loading and unloading machine is ½T Bobcat, 20T excavator, or maximum 100T mast crane.
Jacked Piles
Jack piling is a method of shoring for use under footings laid in weak fill rubble superimposed on the strong stratum, hard clays, or weathered rock. This form of shoring is particularly suitable for limited access situations where there is no room for drilling rigs of any capacity.
The depth that these piles can reach is directly related to the test load that the building can withstand. It is not recommended for residential homes as this method relies on the weight of the building to achieve the required load capacity.
Bored Piles
The bored pile is constructed by digging a hole in the ground using appropriate means such as temporary or permanent casing or percussion or rotation methods of drilling mud. After that, the construction is completed by filling the holes with reinforced concrete.