ABSTRACT: Retaining walls are structural elements that are not a direct part of the frames of a building but have a defined structural function connecting directly with the main structure.
ABSTRACT: Retaining walls are structural elements that are not a direct part of the porticos of a building but that have a defined structural function connecting directly with the main structure.
Types Of Retaining walls
This type of element is built in the basements of structures that have levels below the ground level, or masses of soil, in general, that must be stabilized with these structures, for example, the ground cuts in the tracks.
They are mainly responsible for retaining the soil that is behind them while maintaining its stability. Retaining walls are generally built in reinforced concrete, although materials such as structural masonry are also used.
The structural design of retaining walls must be carried out by qualified professionals who know the resistance and deformation parameters of the wall, the most suitable construction process, the materials, and the mechanical characteristics of the soil.
In those cases in which the ground is very unstable and there are high probabilities of slopes collapsing, screen walls anchored to the ground with steel rods are used, injecting cement mortar. The length of the anchors, the tensioning force, and the construction specifications are determined by geotechnical.
Excavation:
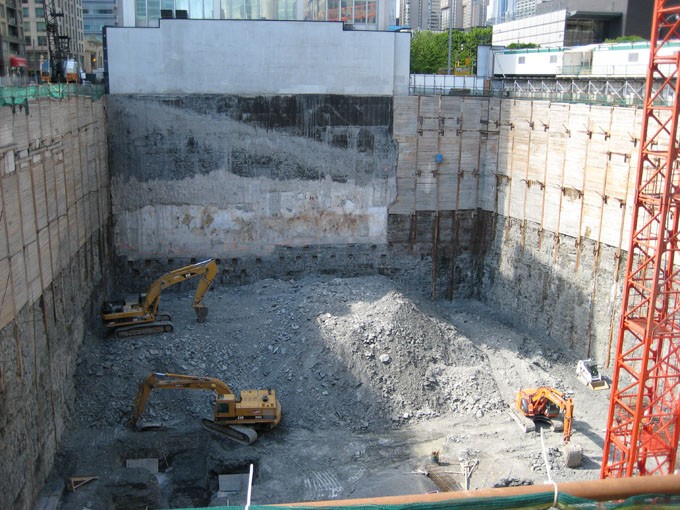
The retaining walls are built as the excavation of basements and foundation work progresses, making it a systematic and fast execution work, without any inconveniences, although special care must be taken due to the great danger that they represent to construction personnel.
When excavations are carried out in buildings with several basements, it is necessary to excavate by level and build the retaining walls for each of the basements. The recommended slopes must be respected to avoid collapses in the excavation, which could delay the work, generate additional and unnecessary costs, and put workers at risk.
Generally, the retaining walls are built in sections, making intercalated modules, digging trenches of constant width, separated at the same distance.

Building Retaining walls
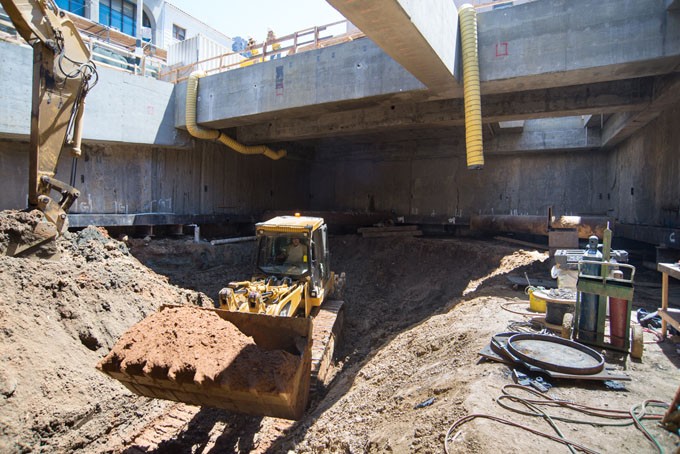
In each module, a structural steel overlap must be left – in the lateral section of the wall and in the lower part in case the excavation continues – to be able to join the adjacent sections of the wall, which will be fused in a second stage. The length of these rods must be specified in the design according to their diameter.
It should be supervised that the structural steel does not get dirty with mud since this can affect the adhesion between the concrete and the steel, modifying its mechanical behavior and causing subsequent damage. The trench can be covered with a thin layer of mortar to increase stability while working on the wall module.
Subsequently, we proceed with the formwork of the wall, taking into account that the forms must be in an optimal and clean state to ensure a good finish on the surface that will be exposed. The thickness of the wall and the covering of the reinforcing steel must be ensured through the use of spacers.
Retaining walls
To pour the concrete into the retaining wall, the use of a hopper or funnel should be considered to prevent the concrete from striking sharply against the walls of the forms, with the consequent segregation.
Generally, the aggregate must be of a small nominal diameter (gravel type), because due to the little space it has, anthills or voids can be generated in the wall.
Usually, concrete pours are made in layers 40 to 50 centimeters high with their corresponding vibrating, also hitting the form with a rubber hammer also called “chipotle” to ensure adequate compaction. The first 15 or 20 centimeters of a wall can be cast with more manageable concrete so that in this way a much easier placement can be made. The consistency of the concrete could also be lowered as the level increases, to compensate for the exudation of the lower layers, and obtain greater durability and uniformity in the wall.
Care must be taken when casting sloping layers since this causes the concrete to segregate and can cause problems of porosity and weakness in the element. At the end of the concrete pouring, the upper level of the concrete should be exceeded by approximately two centimeters because as the concrete sets, it sometimes decreases in height.

To keep in mind
The retaining wall should be temporarily buttressed while the tie is made with the upper floor plate, which will have structural support to retain the fill. In walls whose height exceeds one floor, a tie beam can be placed in the middle and another at the top, to stiffen and connect with the aerial plates of the building. Hooks and ties at the intersection points of the beam and the wall are equally of great importance and must meet the requirements of the standard hook.
The explanatory note of responsibility: The observations contained in this document are informative and should be applied and/or evaluated by the manufacturer or user only if they are considered pertinent. Therefore, these observations do not bind Argos, its subsidiaries, or its subordinates.
“To pour the concrete into the retaining wall, the use of a hopper or funnel should be considered to prevent the concrete from hitting sharply against the walls of the forms, with the consequent segregation “.