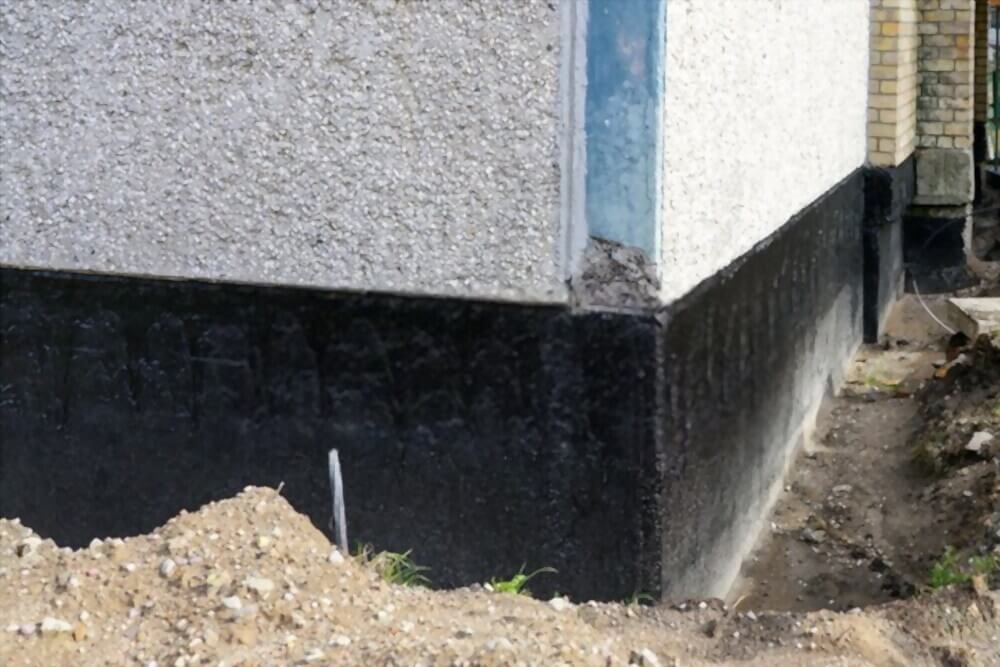
The presence of damp proofing is very necessary to maintain the health of a structure. DPC plays an important role in all types of buildings and it should be necessary to know about the importance, requirements, and properties of DPC. In many of the buildings all over the world, the rising damp may be due to a damaged damp-proof course, or sometimes, there may be not any damp proof course in a building. The repair and the installation of damp proofing course (DPC) prevents the damp rising problems in the buildings, which in turn keeps the walls clean, structurally sound, and free of moisture. Now let’s explore DPC (Damp Proof Course) in more depth.
The most important element in keeping the building strong for a long time is to reduce or maintain the entry of moisture in the building from roofs, floors, or walls. Dampness is usually the presence of moisture in the structure. The dampness reduces the integrity and strength of the structure and creates unhygienic conditions. So in the construction or designing of buildings, the damp proof course or damp protection is quite necessary. DPC or damp proof course is the main method to reduce dampness in the structure by restricting the entry of moisture in the structure.
What is Damp Proofing (DPC)?
Damp Proofing is the name given to the protective layer which is placed between the property and the external ground. The name of DPC indicates the function played by it independent of the materials used for providing a damp proof course.
Reasons Behind the Dampness(Damp proofing)
The main reasons which cause dampness in the buildings are as follows:
- Rain penetration
- Level of site
- Condition of climate
- Improper orientation of the building
- Construction joints in the structure
- Use of low-quality construction materials
- Soil drainage problems
- Entrapped moisture during concreting
- Low-quality concrete used
- Moisture ingress from the ground to the walls
- Rain falling from the top of walls
- Rain effects on the external walls of the building
- Condensation problems
Some of the causes are discussed below for a better understanding of the dampness.
Moisture ingress from the ground to walls
If the soil on which the foundation rests and soil is pervious then moisture finds its way to travel through the structure and it travels constantly. The previous soil is also capable of absorbing moisture so by the capillary action this moisture rises in the walls of buildings from floors. This process is slow but its effects are seen as soon as moisture reaches the walls.
Rain travel from the walls of the building
If the roofs and walls of the buildings are not made of waterproof the water may travel down and it may cause dampness in the building.
Rain falling on the external walls
Mostly in buildings the paints or the interior decorations of the building gets deteriorate due to the dampness entering the building from the rainwater accumulating in the balcony of the building. Therefore, the external walls of the buildings must be treated properly to inhibit the effect of dampness in the building.
Condensation Damp Proofing
The process of condensation may result from dampness in the building, this occurs due to the change in temperature in the inside ad outside of the building which results from the deposition of water onto the roofs, ceilings, and walls of the buildings.
There may be some other reasons which may cause the entrance of moisture in the building, which are
- Improper drainage at the site
- Less perfect roof slope of the building, in cases of flat slopes, water accumulation may occur
- Careless construction activities, which leaves joints in the roof, defective points
- If the orientation of the building is such that there is less entry of sunlight in the building so the water which entered the building previously may take a large amount of time to dry
Effects of Dampness on Building
The effects of dampness in buildings are as follows:
- The ingress of moisture from the walls and ceilings of buildings results in patches in the building or may cause the crumbling of plaster and paints.
- The growth of termites and breeding of mosquitoes may occur due to dampness in the building.
- The warping, buckling, and deforming of woodworks may occur such as doors, windows, wardrobes may warp when they come in contact with damp walls and damp floors.
- The excessive presence of moisture in the building may result in efflorescence in the walls of the houses, which may show up on the bricks or stone stiles. All these things ultimately result in the strength reduction of the walls.
- The dangers of short circuits may increase due to the leakage of electricity resulting from the dampness or moisture in the electrical fittings.
- The metal fittings attached to the walls, roof, and ceilings may corrode and trust dye to the moisture content.
- The plaster of the building may soften or crumble due to the dampness effect on them especially in the case of lime plaster.
- The disintegration of wall decorations such as paintings, puttings may occur due to dampness in the building.
- The floors of the buildings may lose their integrated strength with the ground and may crack because of the loss of adhesion in the ground tiles.
- The presence and increase in the number of termites may occur due to the presence of moisture in the building.
Damp Proofing Specifications
The damp proofing work is performed according to the rules of the specification out the codes and standards, some of these standards are given below:
ATSM D41-78
This standard is based on the use of primer with asphalt for damp proofing and waterproofing.
ASTM D2103-81
This standard is based on the damp proofing measures by the use of polyethylene film and sheeting.
BS 747-77
This gives information about the specification of the roofing felt.
BS 1521-72
This British standard is based on waterproof building materials.
BS 4016-72
This standard states the use of building paper which is of breather type to be used for damp proofing purposes.
Methods of Damp Proofing
There are many methods for making damp proof courses. Some of them are given as follows:
- Use of DPC as a membrane damp proofing
- Integral damp proofing
- Surface treatment
- Cavity wall construction
- Guniting
- Pressure grouting
Membrane damp proofing
In membrane damp proofing, the membrane which is water repellant is placed between the source of dampness and the part of a building that is to be protected from dampness. The materials which may be used in this membrane may bitumen, polythene sheets, felts, cement concrete. The damp proof course may either be placed vertically or horizontally in floors and walls. The following process and cautionary measures must be adopted while providing DPC.
- The mortar bed should be used as a support.
- The surface on which damp proofing course (DPC) is applied should be free from any harmful material and free from any materials that might alter or harm the properties of the damp proof course.
- DPC should be laid continuously on the junctions and corners of the wall and must act as an integral part of the building.
- In the case of the junction of horizontal DPC with the vertical face of the wall, a small amount of cement concrete fillet should be used with a radius of 7.5 cm.
- The DPC should not be exposed to the other side walls which may result in damage to the DPC layer during finishing work and inspection work.
- The DPC (damp proof course) layer should cover the full thickness of the wall.
Integral Damp Proofing
It is the addition of additional waterproofing material to the concrete mix so that it becomes permeable. The principle of using this compound should be such that it acts as a chemical in which they react with the concrete bodies as a waterproof concrete or water repulsive material in which the addition of compound makes it repulsive to the water.
The waterproofing materials or compounds may be used in many forms. some of these forms are to fill the void of concrete by the application of mechanical principle from the compounds made from chalk, talc, or some fillers, which fill the voids of concrete, to be used a waterproof concrete-like alkaline silicate, CaCl2, or as aluminum sulfate, as a water repellant compound ( such as soap, petroleum, oils or fatty acids) which are mixed with compound, to be used as commercially available compounds like public, promo, and silica, etc.
Surface treatment
It is the method of applying the water-repellant materials on the surface which is to be protected from the water penetration such that it inhibits the ingress of moisture. The use of water-repellant sheets such as calcium and aluminum plates are mostly used which are very effective against rainwater penetration.
This method of damp proofing is used when the mixture is properly mixed and it is not done under pressure. The plaster of the wall exposed to the water penetration must be done carefully with some waterproofing compounds such as sodium or potassium silicates, zinc sulfates, or magnesium sulfate.
The surface treatment is generally given good results as compared to other methods. In some cases, the wall and the layers to be protected from dampness are sprayed with water-repellant solutions.
Painting and plastering of the exposed surfaces must be done carefully, using waterproof agents like sodium or potassium silicates, aluminum or zinc sulfates, barium hydroxide and magnesium sulfate, etc. The surface treatment gives better results only when the mixture is superficial and not under pressure. Sometimes walls of stone and brick exposed surfaces are sprayed with water repellent solutions.
Cavity Wall Construction
This wall prevents the penetration of water inside the building by protecting the main wall by an outer skin wall acting as the cavity between two. It is really an effective method of damp proofing.
Damp Proofing by Guniting
It is the method of deposition under pressure and a layer of cement mortar of mix ratio of 1:3 is sprayed or shot on the clean surface from the distance of 75 to 90 cm with the help of a cement gun under pressure. For the perfect application on the surface, the nozzle of the gun should be kept perpendicular to the surface of the application. The mortar should of good consistency and thickness so that it can act as a proper water repellant layer. The mortar should be properly mixed and it should be cured for 14 days.
Pressure Grouting
It the process of forcing cement grout in the place of application as cracks, voids under pressure. The pressure is applied which causes the consolidation of structural components and which increases their resistance towards water penetration. This method is mostly used for reducing the seepage of groundwater through the foundations of the structure.
Characteristics of materials used for damp proofing course (DPC)
The materials used for DPC purposes may have the following properties:
- The material should be strong and able to carry and sustain the superimposed loads that act on it.
- The material should be leakproof.
- It should be impervious to the entry of water so that it stops the moisture penetration in the building.
- It should be flexible enough so that it can easily bear the movements of the structure resulting in cracks in the building.
- It must have high durability and its life span also should equal that of a building.
- It must have a cheap price and it should be readily available in the market.
- The material placement should be in a rigid condition so that it cannot exhibit changes in itself and its properties.
Read Also: Basic Parts of Building Structure and their uses
Damp Proofing Material
The most common materials used for damp proofing purposes are given as below:
- Metal sheets
- Hot bitumen
- Bituminous felts or asphaltic felts
- Sheets and bituminous felts combination
- Bricks
- Stones
- Mortars
- Cement concrete
- Plastic sheets
- Felt
- Polythene sheet
- Junaid waterproof matting
Asphalt (Mastic)
It is made by the addition of asphalt with the sand and mineral fillers up to a code provided temperature. This type of material is strong enough with highly impervious and durability. It can bear high temperatures easily, so it can be easily used in areas where the temperature is higher than room temperature.
Hot Bitumen Damp Proofing
It a type of bitumen that is very hot and it is applied on the concrete bedding and mortars with a thickness of it up to 3mm.
Asphaltic or bituminous felts
This is a very flexible material and it is available in the fo0rm of rolls of various wall thicknesses. It is used for lightweight loads. It is laid on the cement mortar concrete and should be flat layered. It is placed at the full overlap at angles, junctions, and crossing with the overlapping length of 10 cm (4 inches) at the joints. A seal would also be provided at the overlaps.
Sheets and Bituminous felt a combination
The perfect material to be used for the damp proofing course is the combination when lead foil sheets are placed between the asphaltic felts. This type of material is called a lead core. It has many useful properties such as ease of lying, reliability, efficiency, and resistance to cracking
Bricks
When the dampness of the building is not so high then a special type of brick may be used for damp proofing. The water absorption properties of the bricks should be less than 4.5 % of their weight. The application of bricks is done such that they are laid in 2 to 4 courses in cement sand mortar. The joints are also kept open in case of using bricks for DPC.
Stones
In some cases of damp proofing, the sound stones are placed on the full width of walls. Such stones may be of granite, trap, or slates. The mix design ratio of this course is 1:3.
Mortar
The mortar can also be used for DPC purposes by the cement mortar of ratio 1:3. The water used for making the cement mortar should be a form of soft soap and some amount of lime must also be added which may help in increasing the workability of the cement mortar.
Cement Concrete
It is the most used method to be used as a damp proof course, in which the thickness should be between 4 cm to 15 cm. it is placed at the plinth level with the mix design ratio of 1:2:4 or 2:1.5:3. This type of DPC material can restrict the water entry by capillary action. Some amount of hot bitumen is also used in 2 courses which may be used if the dampness is more.
Plastic Sheets
It is a type of DPC material that consists of polythene black in color with a thickness of 0.5 mm to 1 mm. This is usually applied to the wall. There is also a new method of DPC course in which a lead sheet is used with 1: 4 cement mortars. This is a much cheaper method but not permanent.
Metal Sheets
The metal sheets may also be used as a damp proof course. These metals are usually lead copper or aluminum. The lead sheets are the most flexible among all of them. The thickness of these sheets should be such that the weight of the sheet should not be less than 20 kg/m2.
These are similar to bituminous felts. There are many advantages of using lead sheets such as they are completely impervious to moisture, resistant towards corrosion, able to take many complex shapes without any fracture and they are resistant to sliding action.
The copper sheets may also be used for DPC purposes by embedding them into the cement mortar. The copper sheets have many properties like durability, resistance towards dampness, ordinary pressure, and sliding. The aluminum sheets can also be used for this purpose. It is not as beneficial as the lead and copper sheets, so it should be protected with a layer of bitumen for durability.
Felt
The felt is an asphaltic impregnated fiber base. The ply thickness is based on the specification in the drawings. The felts should be smooth enough with proper waterproofing qualities.
Polythene sheet
This polythene sheet is also known as an isolation membrane which is 0.13 mm thick.